Microscope – Let’s split the name into two parts to understand what it actually means. “Micro” means very small (typically not visible to the naked eye) and “scope” means to assess or investigate carefully.
So, the microscope is an instrument that aids users to carefully investigate and assess microscopic organisms and objects that are not visible to the naked eye.
The most important feature of a microscope is that it magnifies the image of the specimen and resolves it better to help the observers see the specimen clearly to carry out their experiments.
Although Zacharias and Hans Janssen are credited with the invention of the first microscope in 1590, the first practical microscope was constructed by Anton Van Leeuwenhoek.
Microscopes have varied uses in various fields such as:
- Education
- Research in Medical Sciences and Life Sciences
- Industrial Applications
- Biology
- Forensics
Education:
Various educational institutions like schools, colleges, universities use microscope in their laboratories to examine microscopic organisms and teach their students the uses of microscopes.
Students use the microscopes to learn new things and understand the basic building blocks of life and matter
Research in Medical Sciences and Life Sciences:
Microscopes aid in identifying viruses, bacteria and other microbial organisms and help the researchers in studying about diseases and find a cure to them.
Researchers and pathologists examine several specimens a day to understand the underlying cause to a disease to enable doctors to give the right treatment to their patients
Industrial Applications:
Microscopes are used in industrial setup to facilitate quality control, aid manufacturing processes such as soldering, watch making etc. Microscopes are also used for inspection of products in a production line.
Biology:
Microscopes find application in studying samples at a cellular level in biology. Microscopes are useful in studying both plant life and animal life at a cellular level and thus find application in botany as well as zoology.
Forensics:
Microscopes help forensic professionals in examining hair, fragments, skin cells, and evidence material to determine the exact cause of an event and help the law enforcement and investigating agencies in nabbing the culprits and bringing them to justice.
We will now classify the major types of microscopes based on their application in the aforementioned fields and more especially in the widely used biology domain. The major types of microscopes include
- Simple Microscope
- Compound Microscope
- Electron Microscope
- Phase-contrast Microscope
- Interference Microscope
Simple Microscope
Simple microscope is a magnification apparatus that uses a combination of double convex lens to form an enlarged, erect image of a specimen.
The working principle of a simple microscope is that when a lens is held close to the eye, a virtual, magnified and erect image of a specimen is formed at the least possible distance from which a human eye can discern objects clearly.
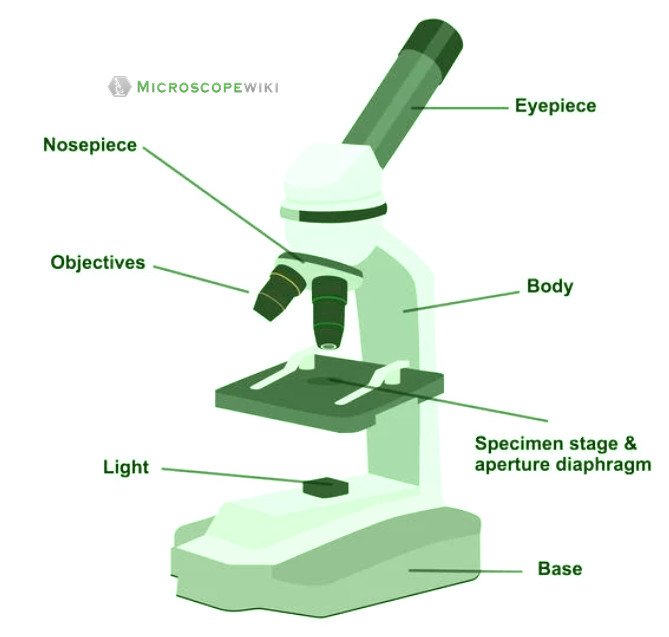
Simple microscope labeled diagram
Simple microscope functions
- It is used in industrial applications like:
- Watchmakers to assemble watches
- Cloth industry to count the number of threads or fibers in a cloth
- Jewelers to examine the finer parts of jewelry
- Miniature artists to examine and build their work
- Also used to inspect finer details on products
- It finds application in the study of microorganisms like fungi, algae and other biological specimens
- Used by dermatologists to examine various skin diseases
- By pedologists to examine and study various soil samples
- By students in the school to have a basic and beginners knowledge about microscopes
Compound Microscope
A compound microscope uses a combination of lenses coupled with an artificial light source to magnify an object at various zoom levels to study the object.
A compound microscope:
- Is used to view samples that are not visible to the naked eye
- Uses two types of lenses – Objective and ocular lenses
- Has a higher level of magnification – Typically up to 2000x
- Is used in hospitals and forensic labs by scientists, biologists and researchers to study micro organisms
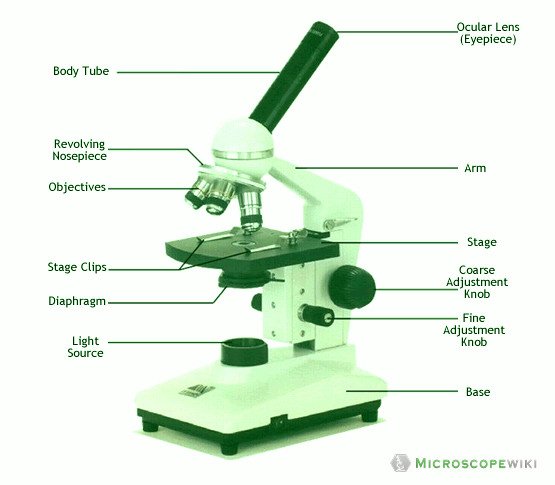
Compound microscope labeled diagram
Compound microscope functions:
- It finds great application in areas of pathology, pedology, forensics etc
- Its greater order of magnification allows for deeper study of microbial organisms to
- Detect the cause of diseases
- Study the mineral composition in soils
- Examine evidences collected in crime scenes by forensics.
- Helps students conduct their academic experiments.
- Helps in understanding various organisms thriving on the plant cells to study and eradicate them if need be.
Electron Microscope
Atypical to the common microscopes, an electron microscope uses a beam of accelerated electrons instead of a light source to illuminate the specimen.
The shorter wavelength of electrons compared to visible light photons helps the observer achieve a very high resolving power compared to normal microscopes thereby aiding observers to see very tiny objects clearly.
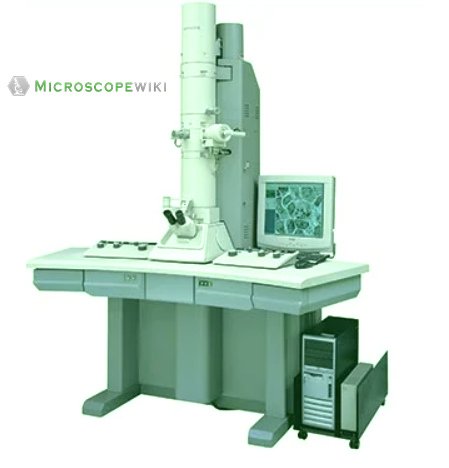

Electron microscope labeled diagram
The different types of electron microscopes are:
- Transmission Electron Microscope
- Scanning Electron Microscope
- Reflection Electron Microscope
- Scanning transmission electron microscope
- Scanning tunneling microscopy
Electron microscope functions:
- Semiconductors and Data Storage Industry
- Failure Analysis
- Checking for defects
- Circuit Editing
- Life Sciences and Biology
- Imaging tissue
- Toxicology
- Particle analysis
- Structural Biology
- Industrial Sectors
- Forensics
- Mining
- Food Science
- Petrochemical/Chemical
Phase-contrast Microscope
Phase-contrast microscopes are more advanced microscopes used to examine and study transparent specimens such as latex dispersions, tissue slices, sub-cellular particles, lithographic patterns, microorganisms and living cells among others.
These microscopes work on the principle called contrast-enhancing technique that is utilized to produce high-contrast images to view them with more accuracy and clarity.
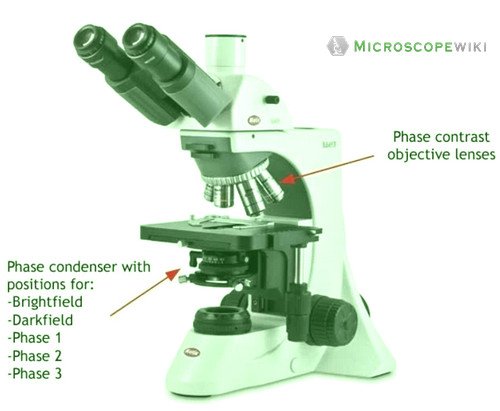
Phase-contrast microscope labeled diagram
Phase-contrast microscope functions:
Its applications areas include
- In cases where the specimen is colorless and is very tiny
- In biology to conduct cellular level examination of microorganisms that can’t be visualized using the bright field microscopy
Interference Microscope
This is an advanced microscope that has specific application in viewing, observing and measuring the optical thickness and phase of completely transparent specimens and objects. A tiny interferometer is used and a specimen is placed on beam path of it.
This path is split and then rejoined to create two superimposed images of the specimen in focus. Using the variation in brightness of the images, the phase and optical thickness of the specimen are measured.
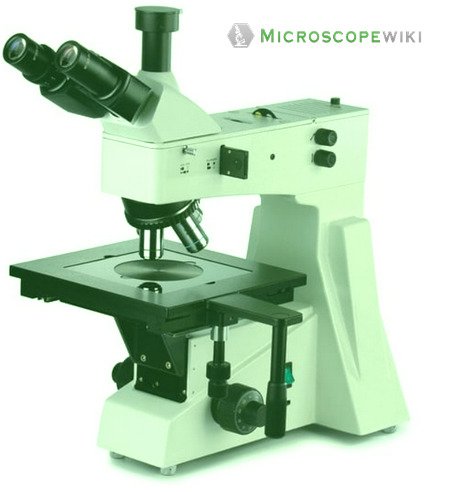

Interference microscope labeled diagram
Interference Microscope functions:
It finds use in
- Medicine
- Biology
- Biomedical research
References:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/electron-microscopes
- https://microbenotes.com/simple-microscope-principle-instrumentation-and-applications/
- https://microbenotes.com/compound-microscope-principle-instrumentation-and-applications/
- https://www.biologydiscussion.com/biology/5-important-types-of-microscopes-used-in-biology-with-diagram/2635
- https://www.msnucleus.org/membership/html/jh/biological/microscopes/lesson2/microscopes2d.html
- https://toolboom.com/en/articles-and-video/types-of-microscopes/
- https://www.nanoscience.com/techniques/scanning-electron-microscopy/
- https://www.microscopyu.com/techniques/phase-contrast/introduction-to-phase-contrast-microscopy
- https://spie.org/news/4707-interference-microscopy-offers-new-applications-for-biomedical-research?SSO=1
- https://www.photonics.com/EDU/interference_microscope/d4803