A dark field microscope operates on the opposite principle of a brightfield microscope, and the entire field of view appears dark when there is no specimen and once a specimen is placed, it appears bright over this dark background. Hence the name dark field microscope.
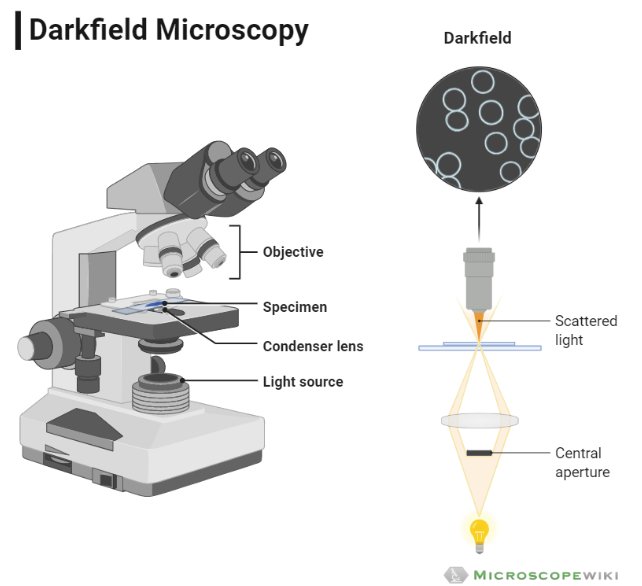
What is Dark field microscope
A dark field microscope is similar to the bright field microscope, but the major difference is that in a bright field microscope the specimen is illuminated, and the refracted light is used to form an image of the specimen.
See : Difference Between Brightfield and Darkfield Microscope
However, when the specimen can’t refract light, it needs to be stained in order to view under a bright field microscope which sometimes kills the specimen.
It is in such cases, dark field microscope can be used which doesn’t illuminate the specimen, rather creates a bright image against the dark background thereby making it useful to observe unstained and live specimens.
Working Principle and Diagram
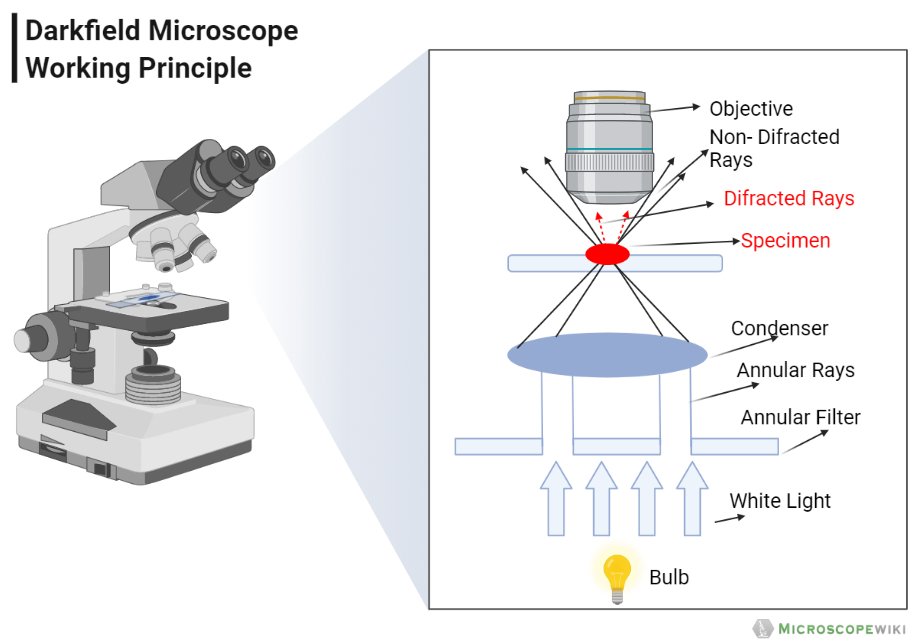
- In a dark field microscope, the condenser is designed in such a way that it forms a hollow cone of light and the objective lens is placed in the dark hollow of this cone and the light travels around the objective lens but doesn’t enter the hollow cone thus creating a dark field for viewer when there is no sample to be viewed.
- But when a specimen is placed on the stage, it appears bright against the dark ground thereby making it magnified and visible.
- In simple words, the specimen is backlighted to make it more visible rather than collecting the refracted light form the specimen.
Applications
- It is used in the field of microbiology and parasite study where observing live organisms is a necessity
- It is used to observe the internal structures of microorganisms considerable
- It is used to observe live and unstained specimens
- It is used to observe blood cells and also algae
- It can be used to observe invertebrates like shrimps and others
- It is typically used to examine exterior details like grain boundaries, edges etc. than the internal structure of specimens.
Advantages of Darkfield Microscope
- Darkfield microscopy is a relatively easy and a very effective technique
- It enables viewing live organisms unlike a brightfield microscope
- It doesn’t require staining the specimen to view thereby allowing for contamination free magnification
- Darkfield microscopy is easy to achieve, and a normal optical microscope can be converted to a darkfield microscope with little changes
- The quality of the images is excellent, given the simple technique used to achieve magnification
Disadvantages of Darkfield Microscope
- The need to illuminate the sample strongly may damage it
- Another major limitation is the low light levels that are seen in the final magnified image
- It is not a reliable tool to obtain the accurate measurement of the specimens
- Specimens that have water or oil are not replicated properly because of the fact that air bubbles in the liquids distort the image
- The quality and preparatory work on the specimens needs to be excellent. Otherwise, the accuracy and contrast is affected thereby damaging the quality of image obtained.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the difference between darkfield microscope and brightfield microscope?
The major difference is that a bright-field microscope uses light rays to create a dark image against a bright background while a dark field microscope creates a bright image against a dark background.
Q2. What is the cost of a darkfield microscope?
The cost of a darkfield microscope ranges from 150US$ to 200US$
Q3. Similarity between brightfield microscope and darkfield microscope
The most important similarity is that both are optical microscopes that employ light to illuminate a specimen and create a magnified image but the way the light is employed is different.
References:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/nursing-and-health-professions/dark-field-microscope
- https://www.microscopyu.com/techniques/stereomicroscopy/darkfield-illumination
- https://www.ruf.rice.edu/~bioslabs/methods/microscopy/dfield.html
- https://microbeonline.com/dark-field-microscopy/
- https://microbenotes.com/darkfield-microscopy/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dark-field_microscopy
- https://microbiologynote.com/darkfield-microscope/