While a digital microscope may accomplish the same duties as an optical microscope, it also has additional advantages. A digital microscope does not have an eyepiece and instead uses a digital camera. Digital microscopes can display the findings in real-time by connecting to a computer monitor.
To know more about the digital microscope and its significance, keep on reading below.
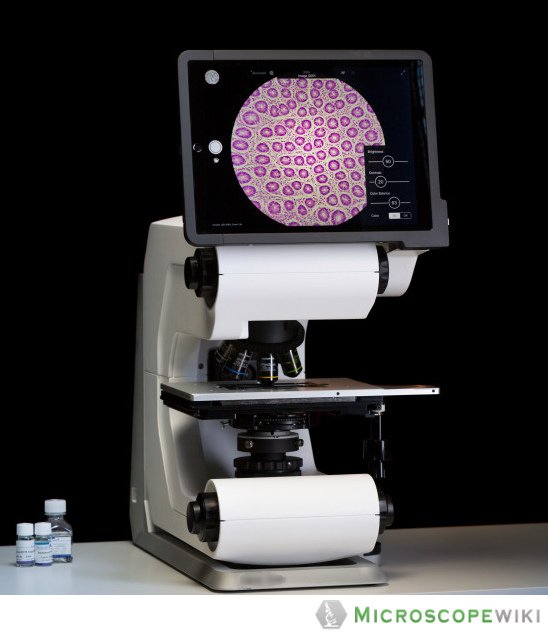

What is a digital microscope and how does it work?
A digital microscope is a useful instrument for inspecting and analyzing a variety of things, from small electronic components to larger ones. It outputs images it has collected to a computer monitor using optics and a digital camera.
It ranges in complexity from straightforward portable models to sophisticated systems that provide a number of observational techniques and measurement capabilities. Numerous digital microscopes make use of sophisticated computer software. Some of this software includes tools that do the following tasks
- Recording videos
- Editing video footages
- Adjusting photos
- Analyzing 3D samples
- Obtaining measurements
- Producing reports
What are the common applications of digital microscopes?
Many different fields, including research, education, the industrial sector, forensics, and medicine use digital microscopes. Here are a few typical examples:
Here are a few typical examples.
- vehicle brake pad inspection
- Identifying fake documents for law enforcement
- Examining the connecting pins
- In the production sector
- Inspecting the manufacture of semiconductor wire bonds
- Enhancing QA/QC procedures in the industry
- Calculating the number of flaws in the car painting procedure
- Ensuring quality/quality analysis
Digital microscopes are vast and they are not created equally. Look for a model with features that fit your particular application if you want to get the maximum benefit of a digital microscope.
With certain digital microscopes, you can switch between observational techniques without switching lenses. This saves time when inspecting brake pads on automobiles because inspectors frequently experiment with several observation techniques to determine which one is most effective.
Types of Digital Microscope
There are various types of digital microscopes. The most commonly used include the following
Fluorescence Digital Microscope
It is a digital microscope that uses fluorescence as the primary light source to generate images.
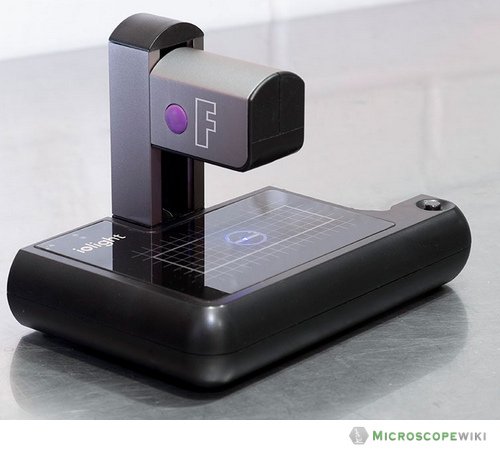

Source: iolight.co.uk
Handheld Digital Microscope
As the name suggests, it’s a new type of digital camera that comes with a tiny handheld system. It is commonly used for forensics and surface inspection.
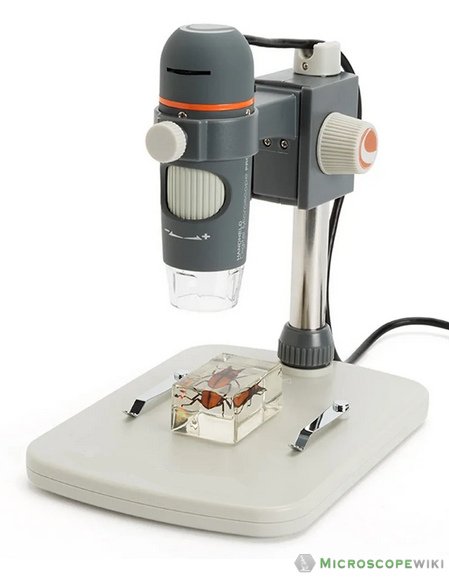
USB digital microscope
It’s a type of digital microscope that has a camera attached permanently. Unlike other digital microscopes, you cannot remove the camera of a USB microscope.

Source
Portable digital microscope
This type of digital microscope is smaller than usual and comes with wireless capabilities. It is used for imaging hard-to-reach surfaces and you can find it typically in the medical setting, dermatology applications, and field inspections.

Digital Microscopes’ benefits and advantages
- Ease of collaboration – Digital microscopes make it simple to communicate information with colleagues because they display images on a screen.
- Better magnification – Compared to typical optical microscopes, digital microscopes have higher magnification. The reason is that digital microscopes base their magnification calculations on the size of the computer monitor. In contrast, optical microscopes multiply the eyepiece and lens magnifications to determine the magnification.
- Optimum comfort – The days of spending hours gazing through an eyepiece are long gone. Instead, you can watch a specimen on the monitor display while sitting comfortably. This results in a more ergonomic workplace.
- Better image quality – Digital microscopes can show an image directly onto the digital microscope camera enabling it to produce high-quality images. Other features, such as anti-halation to lessen glare, better color depth and contrast using the high dynamic range, the capacity to produce all-in-focus images outside of the field of view, and other valuable options such as angled lighting lead to better image texture. In fact, better than what you can see through the eyepieces.
- Image storage – Captured images using a digital microscope are stored on a computer hard disk or other storage devices. The photographs can then be used as references and for in-depth report creation.
- Ease of operation – In general, digital microscopes are simpler to use than conventional optical microscopes. You may start working right away, which makes the work easier and more efficient.
Digital Microscope’s Resolution
A typical 2-megapixel CCD in a digital microscope produces a picture with a resolution of 1600 by 1200 pixels. In this instance, the digital microscope camera lens’ field of view determines the image resolution. It is possible to determine the estimated pixel resolution by dividing the horizontal field of vision by 1600.
A sub-pixel image can be created to increase image resolution. Higher-quality photos can be obtained using the pixel shift method. In this technique, the CCD is physically moved by an actuator in order to take several overlapping photos at once. To create images with a sub-pixel resolution, these numerous photos are merged with those taken within the microscope.
This process gives sub-pixel information, and it is also well-known that sub-pixel information can be obtained by averaging a standard image. Software that is specifically made to improve monitor image resolution is available.
2D measurement
Digital microscopic systems, even expensive ones, typically measure the given material in two dimensions. Onscreen, these measures are made by merely determining the separation between each pixel. This can deliver different measurements such as the following
- Length
- Width
- Circles
- Diagonal
- Other relevant structural attributes
- The number of particles can also be counted by some digital microscopic techniques.
3D measurement
Certain cutting-edge digital microscopic devices can provide 3D measurements. Image stacking is utilized to achieve this. With the aid of a step motor, the microscopic system moves the sample’s pictures from the lowest focus plane in the field of view of the lens to the finest focal plane.
Calculations can then be performed using 3D models, however, the accuracy has something to do with the camera’s depth of field and step motor.
The Differences Between Optical and Digital Microscopes
| Point of Comparison | Optical Microscope | Digital Microscope |
|---|---|---|
| How magnification is obtained | Lens system (eyepieces and objective lenses) | Digital microscope camera (produces real-time magnified image through optical lenses) |
| Depth of field | Becomes shallower as the magnification gets higher | 20 times more depth of field than optical microscope |
| Three-dimensional imaging | 2 Dimensional (difficult to define surface characteristics) | 3 Dimensional (fully focused images) |
| Variable-angle observation capability | None | Delivers 360 degrees observation |
| Quantitative data | Doesn’t provide quantitative data and other relevant measurements | Comes with built-in measurement tools giving measurements in real-time |
| Data sharing | Not possible | Can record images and store on-site. |
Frequently asked Questions
Q1. Are digital microscope images of samples equivalent to those captured with eyepieces?
The image is the same in concept, but there is a variation in the field of view depending on the eyepiece and the type of digital camera used. There is one significant distinction, though: using a stereo microscope’s binocular eyepieces to see a sample gives you a sense of depth that a digital microscope’s 2D image cannot directly provide.
Q2. Is using a digital microscope simpler than using an eyepiece-equipped microscope?
Inexperienced individuals can acquire photos of a sample more quickly and easily with the use of a digital microscope. The primary cause is that using a typical microscope, which requires putting it up, adjusting it, and looking at the material through its eyepieces, takes some getting accustomed to.
Q3. What are the digital microscopes limitations?
When opposed to stereo or compound microscopes, for example, a digital microscope’s obvious drawback is the requirement for a power connection. For digital microscopes, the picture of the sample is always shown on a monitor due to the absence of eyepieces.
Thus, a minimum of one power cable is required. Digital microscopes typically also require a PC connection or, at the very least, a built-in viewing screen. Customers still have the choice to view their sample through eyepieces when using traditional microscopes.
Q4. Does digital microscope have built-in software?
Digital microscope comes with a built-in measurement software, which can be used for comprehensive examination. This feature makes measurement and data collection process easy, convenient, and quick. It also enables the digital microscope to be used in various applications such as in industrial, art, and medical inspections.
References
- https://www.leica-microsystems.com/science-lab/what-you-always-wanted-to-know-about-digital-microscopy-but-never-got-around-to-asking/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_microscope
- https://www.qualitymag.com/articles/95957-what-is-a-digital-microscope
- https://lambdageeks.com/digital-microscope/
- https://tagarno.com/what-is-a-digital-microscope/
- https://www.allthescience.org/what-are-digital-microscopes.htm
- https://microscopeinternational.com/what-is-a-digital-microscope/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/nursing-and-health-professions/digital-microscope
- https://www.microscope.com/education-center/five-things-you-should-know/about-digital-microscopes
- https://microscope-microscope.org/microscope-info/microscope-buyers-guide/digital-high-power-microscope-buyers-guide/